Revolutionizing Healthcare with Biotechnology: How Genetic Engineering and Biopharmaceuticals are Transforming Medicine
Picture a future where diseases are eradicated, chronic conditions are effectively managed, and personalized treatments take center stage. This may sound like the stuff of science fiction, but thanks to the remarkable advancements in biotechnology, this vision is becoming a reality.
In this blog post, we will explore how genetic engineering and biopharmaceuticals are revolutionizing healthcare as we know it. From understanding what technology entails to delving into its history and current applications in medicine, we’ll uncover the immense potential that lies within these groundbreaking fields.
So get ready to embark on a journey through the fascinating world of biotechnology – where scientific innovation meets improved patient outcomes! Let’s dive right in!
What is Biotechnology?
Biotechnology, at its core, is the application of scientific knowledge and techniques to manipulate living organisms or their components for various practical purposes. It encompasses a wide range of disciplines including genetics, molecular biology, biochemistry, and engineering.
In the context of healthcare, biotechnology plays a pivotal role in advancing medical treatments and therapies. By harnessing the power of genetic engineering and biopharmaceuticals, scientists are able to develop innovative solutions that target specific diseases with greater precision.
Genetic engineering involves manipulating an organism’s DNA to introduce new traits or modify existing ones. This technique has opened up endless possibilities in medicine – from producing genetically modified crops that can resist pests to developing gene therapies that can correct genetic disorders.
On the other hand, biopharmaceuticals refer to pharmaceutical drugs derived from biological sources such as proteins and nucleic acids. Unlike traditional chemical-based drugs, biopharmaceuticals offer targeted approaches with fewer side effects as they mimic natural substances found within our bodies.
The field of biotechnology continues to push boundaries by unlocking new avenues for drug discovery, disease diagnosis, and personalized medicine. With advancements like CRISPR-Cas9 technology enabling precise gene editing and bioinformatics aiding in analyzing vast amounts of genomic data quickly – we are witnessing an era where tailored treatment plans based on individual patient needs are becoming increasingly possible.
As we delve deeper into understanding what makes us who we are at a molecular level through genomics research, it becomes evident that technology holds immense potential for transforming healthcare as we know it. The ability to unravel intricate biological processes allows us not only to treat diseases more effectively but also to prevent them altogether.
In conclusion (not concluding): Biotechnology is revolutionizing healthcare by leveraging genetic engineering techniques and harnessing the power of biopharmaceuticals. Its applications range from targeted drug delivery systems to cutting-edge gene therapies aimed at correcting genetic abnormalities. As this field continues to evolve rapidly with groundbreaking discoveries on the horizon, we can expect a future where personalized medicine becomes the new norm.
History of Biotechnology
Biotechnology has a rich and fascinating history that dates back thousands of years. It all began with the early practices of agriculture, where humans started selectively breeding plants and animals to produce desired traits. This can be seen as the earliest form of genetic engineering.
Fast forward to the 20th century, and we see significant advancements in technology. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the structure of DNA, which laid the foundation for understanding genetics on a molecular level. This breakthrough opened up new possibilities for manipulating genes and paved the way for modern technology.
In the 1970s, scientists developed recombinant DNA technology, allowing them to combine genetic material from different sources into one organism. This technique revolutionized genetic engineering by enabling scientists to create organisms with specific traits or produce valuable proteins such as insulin or growth hormones.
Since then, technology has continued to evolve rapidly. The advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies has made it possible to decode entire genomes quickly and cost-effectively. This has led to groundbreaking discoveries in genomics research and personalized medicine.
The field of biopharmaceuticals also emerged during this time. Biopharmaceuticals are drugs produced using living organisms or parts thereof – think vaccines or therapeutic antibodies derived from genetically modified cells.
Today, biotechnology is at the forefront of medical innovation. Scientists are developing gene therapies that have shown promising results in treating previously incurable diseases like certain types of cancer or genetic disorders.
As we look back on its history, it becomes clear that technology has come a long way since its humble beginnings in agriculture. With each new breakthrough comes endless possibilities for improving human health and transforming medicine as we know it.
How is Biotechnology Used in Healthcare?
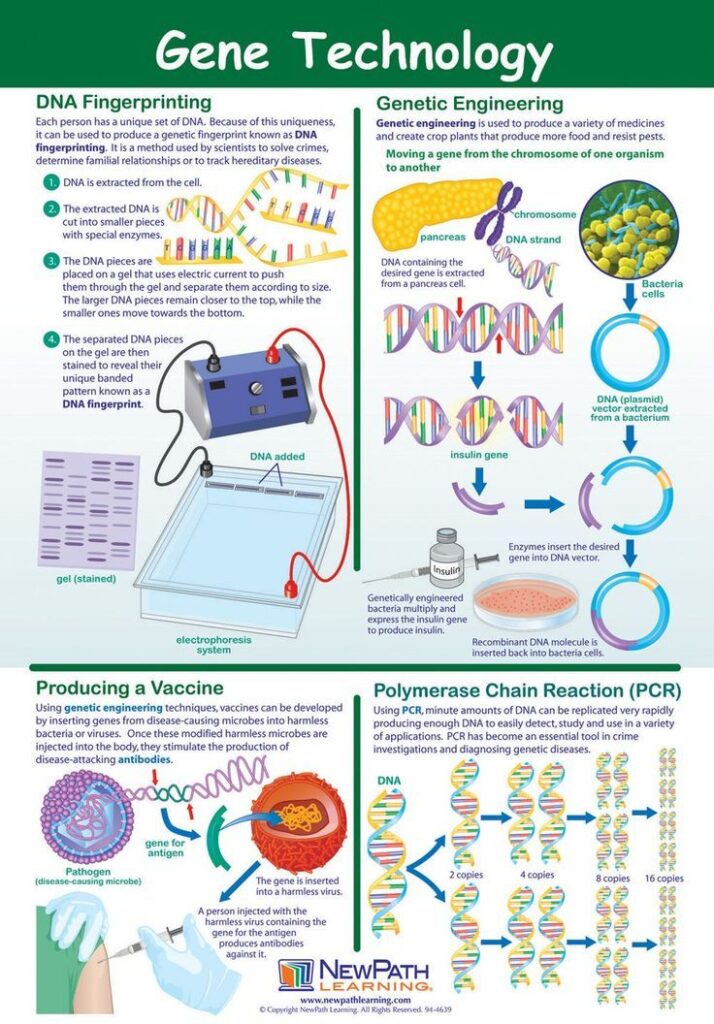
Biotechnology has revolutionized the field of healthcare, offering innovative solutions to diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases. One of the ways technology is used in healthcare is through genetic engineering techniques. By manipulating an organism’s DNA, scientists can create new medical therapies that target specific genetic mutations or produce important biomolecules.
One application of technology in healthcare is the production of biopharmaceuticals. These are drugs derived from living organisms such as bacteria or yeast that have been genetically modified to produce therapeutic proteins. Biopharmaceuticals offer targeted treatments for a wide range of conditions including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and rare genetic diseases.
Another way technology is transforming healthcare is through gene therapy. This cutting-edge approach involves introducing healthy genes into a patient’s cells to correct genetic abnormalities that cause disease. Gene therapy holds promise for treating inherited disorders like cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy.
In addition to therapeutics, technology plays a crucial role in diagnostics. Techniques like polymerase chain reaction (PCR) allow scientists to amplify small amounts of DNA for analysis, enabling early detection and monitoring of diseases such as HIV/AIDS and certain types of cancers.
Furthermore, biotechnology contributes to personalized medicine by allowing doctors to tailor treatments based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup. This approach increases treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects.
The use of biotechnology in healthcare represents a major advancement in medicine. It provides targeted therapies, improved diagnostics capabilities, and personalized treatment options that were unimaginable just decades ago.
Pros and Cons of Biotechnology in Healthcare
Biotechnology has opened up a world of possibilities in the field of healthcare. By harnessing the power of genetic engineering and biopharmaceuticals, scientists have been able to develop new treatments and therapies that were once unimaginable. However, like any other scientific advancement, there are both pros and cons to consider.
On the pro side, technology has revolutionized personalized medicine. With advancements in genetic engineering, doctors can now tailor treatment plans based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup. This means more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Another advantage is the ability to produce biopharmaceuticals through recombinant DNA technology. These drugs are highly specific and target diseases at a molecular level, leading to better outcomes for patients.
Additionally, biotechnology has facilitated breakthroughs in disease prevention through vaccines. Scientists can now engineer vaccines using harmless fragments of pathogens or even synthetic DNA to stimulate immune responses without causing illness.
However, it’s important not to overlook the potential drawbacks of technology in healthcare. One concern is the high cost associated with developing these advanced treatments. The research and development process for new drugs can be lengthy and expensive, making them inaccessible to many people who need them most.
There are also ethical concerns surrounding genetic engineering, particularly when it comes to manipulating human embryos or altering genes that could be passed down through generations.
Furthermore, there is always a risk involved when introducing genetically modified organisms into ecosystems or using them for large-scale agricultural purposes.
In conclusion, biotechnology holds immense promise for transforming medicine by leveraging genetic engineering techniques and producing innovative biopharmaceuticals.
However, it is crucial that we carefully consider both the advantages and disadvantages before fully embracing these advancements. By weighing all perspectives, we can ensure that we maximize the benefits while minimizing any potential risks associated with this rapidly evolving field.
The Future of Biotechnology in Healthcare
One area where technology is expected to have a significant impact is personalized medicine. By analyzing an individual’s genetic makeup, doctors can tailor treatments specifically to their unique needs. This approach has the potential to greatly improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects.
Furthermore, gene editing technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 offer exciting possibilities for curing diseases at the DNA level. Researchers are exploring how these tools can be used to correct genetic mutations responsible for conditions such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell disease.
In addition, technology is likely to play a crucial role in the development of innovative therapies for cancer. Immunotherapies that harness the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells have already shown promising results, and ongoing research aims to refine these approaches further.
Looking ahead, advancements in technology may also lead to breakthroughs in regenerative medicine, enabling damaged tissues or organs to be repaired or replaced with lab-grown alternatives.
However, it’s important not only to highlight the potential benefits but also to consider the ethical implications and potential risks associated with these technologies. Striking a balance between innovation and ensuring safety will be key moving forward.
While there are still challenges ahead, it’s clear that the future of biotechnology in healthcare holds great promise for improving patient outcomes and transforming our approach to treating diseases. It will require continued investment in research and development as well as collaboration between scientists, clinicians, regulatory bodies, and policymakers – all working together towards making these advancements accessible while prioritizing patient safety
Conclusion
Biotechnology has revolutionized healthcare in ways that were once unimaginable. Through the fields of genetic engineering and biopharmaceuticals, we have witnessed remarkable advancements in medicine and improved patient outcomes.
The history of biotechnology is rich with scientific discoveries and breakthroughs. From the discovery of DNA to the development of recombinant DNA technology, scientists have laid a solid foundation for the field’s progress. Today, technology plays a pivotal role in healthcare by providing innovative solutions to complex medical challenges.
In healthcare, technology offers numerous applications that are transforming how we diagnose and treat diseases. Genetic engineering allows us to manipulate genes, leading to targeted therapies for genetic disorders or personalized medicine tailored to individual patients. Biopharmaceuticals harness living organisms and their products to create effective drugs with fewer side effects than traditional pharmaceuticals.
Of course, like any other field, there are pros and cons associated with technology in healthcare. On one hand, it has opened doors for groundbreaking treatments such as gene therapies that can potentially cure previously untreatable conditions. On the other hand, concerns about ethics, safety regulations, and access to these advanced treatments need careful consideration.
Looking ahead into the future of biotechnology in healthcare holds immense promise. With ongoing research efforts focused on understanding human genetics better, we are likely to witness even more precise diagnostic tools and targeted therapies emerging rapidly. The potential applications seem endless – from creating vaccines against previously incurable infectious diseases to developing regenerative medicines capable of replacing damaged tissues or organs.
In conclusion (without using “in conclusion”), genetic engineering and biopharmaceuticals have undoubtedly revolutionized modern medicine through innovations enabled by advances in technology. As researchers continue pushing boundaries further each day while addressing ethical considerations along the way—we stand at an exciting juncture where cutting-edge technologies offer new hope for patients worldwide.

2 comments